Blog
What is Reinforced Concrete (RC)?

What is Reinforced Concrete (RC)?
Reinforced concrete, also known as “béton armé” (derived from the French word Béton armé) is a very durable building material; this article examines it.
In many constructions, using regular concrete is not sufficient, and for greater strength, more resistant or so-called reinforced concrete is used. In fact, to increase the strength of reinforced concrete, steel bars are placed in it, which have very good resistance to tensile forces.
Reinforced concrete (RC) is a type of composite material strengthened with steel reinforcements and used in the construction of modern structures. Ordinary concrete cannot withstand many stresses such as vibrational stresses, wind loads, etc. Therefore, by reinforcing the concrete with steel reinforcements such as rebar, rods, and cables, we create reinforced concrete (RC), which compensates for the low tensile strength and ductility of regular concrete.
Get to know the types of reinforced concrete
In the following, we will examine different types of reinforced concrete and provide important information about their applications and advantages. In general, concrete is categorized into two types: concrete reinforced with rebar and concrete reinforced with fibers.
-
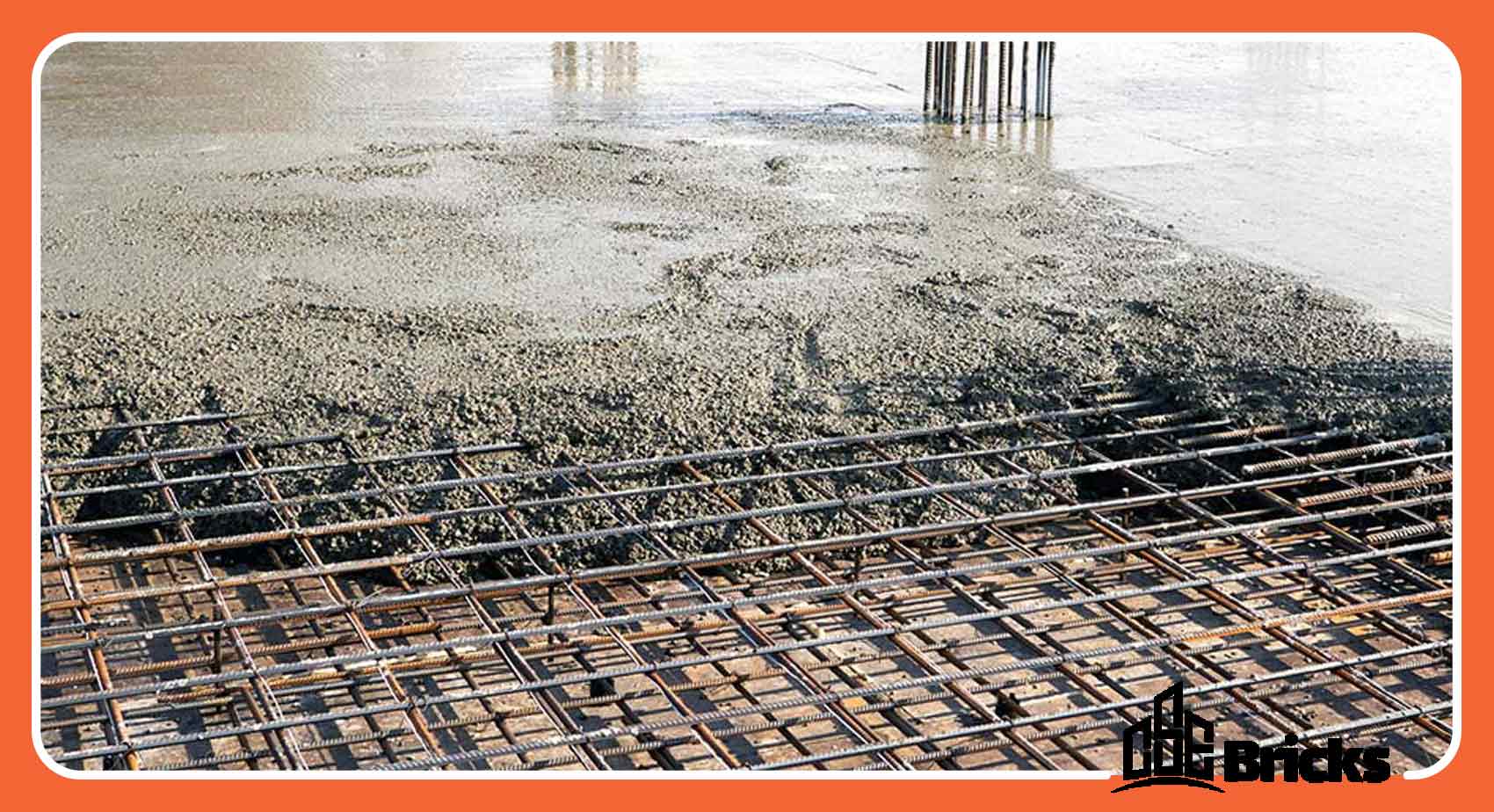
Reinforced Concrete with Rebar
The most common method of producing RC (Reinforced Concrete) is by combining it with rebar. In this type of concrete, rebar is used as a reinforcing element. Typically, the rebar used in concrete is made of steel and can be either threaded or unthreaded, or made of glass and polymer. However, the steel type is most commonly used because the coefficient of expansion of steel and concrete is more similar, making them more resistant to damage when used together.
-
Pre-Tensioned and Post-Tensioned Concrete
Another type of reinforced concrete used in large construction projects is pre-tensioned concrete. Pre-tensioned concrete is made through pre-tensioning or post-tensioning processes on steel alloy cables and tendons. But what is pre-tensioning? Pre-tensioning involves applying internal stress to the concrete in the opposite direction of external forces to neutralize them. In pre-tensioned concrete, the cables are tensioned within the concrete while it is still wet, and then the concrete is poured. As the concrete starts to set, the cables put pressure on the concrete. In post-tensioned concrete, the tensioning process is done after the concrete has set. The advantages of this type of reinforced concrete include its high inherent compressive strength, reduced structural weight, reduced shear stresses, and reduced required cross-sectional area.
-
Precast Reinforced Concrete
Precast concrete is named as such because it is produced in a controlled factory environment and under supervision. For this reason, its construction speed is much faster than other types of concrete. This type of concrete is used in projects such as columns, wall construction and building facades, structural members, bridges, subway tunnels, water tanks, and more. Precast concrete has advantages such as implementing structural elements on the ground rather than at height, controlling the setting of concrete, and executing in controlled environments away from adverse weather conditions.
-
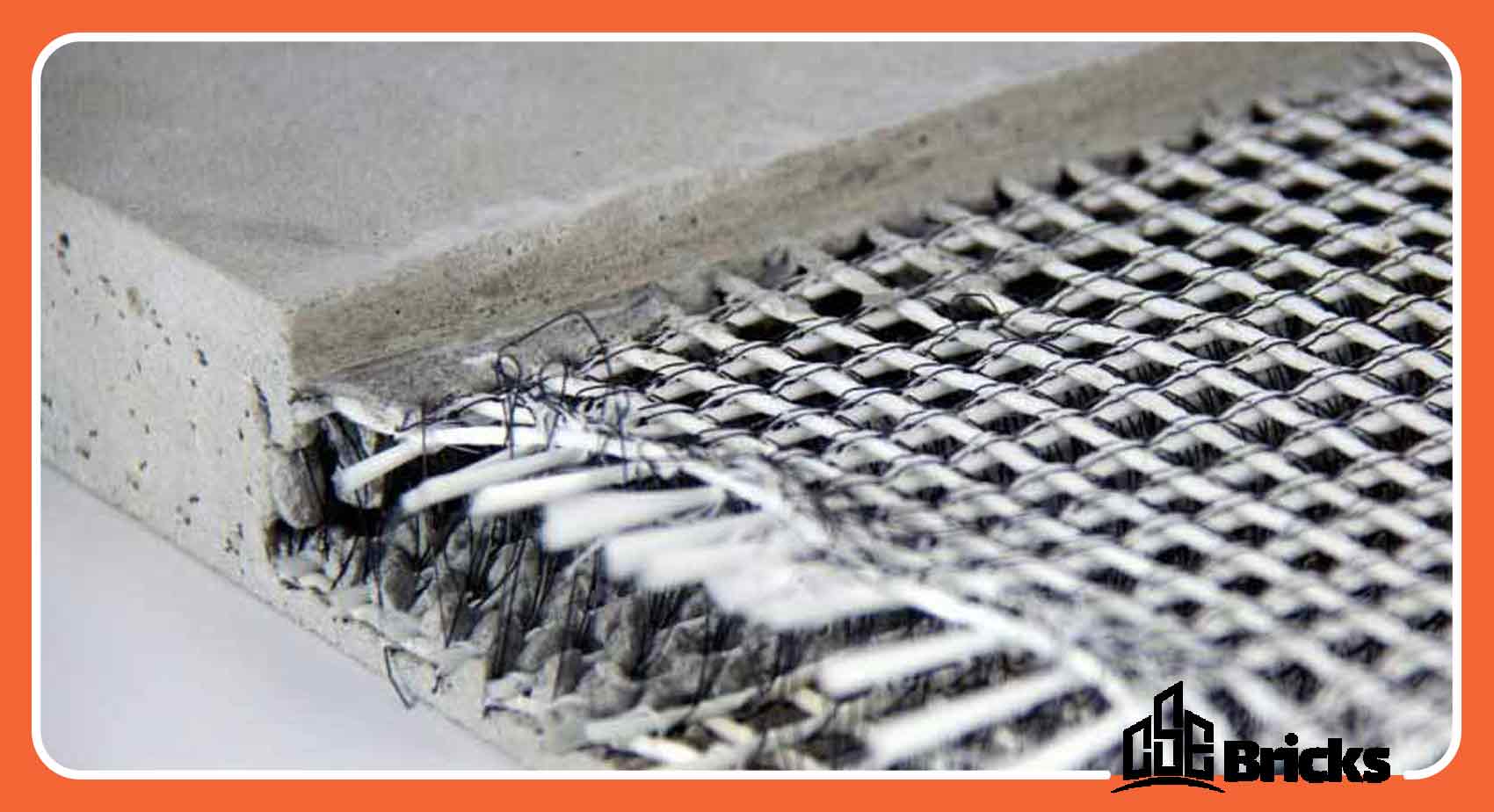
Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
For greater concrete integrity and to prevent moisture and water ingress, it can be reinforced with fibers, known as fiber-reinforced concrete. This type of concrete is often produced by combining cement mortar and separate steel fibers. The separate fibers used in it can also be mesh, woven fibers, rods, and long wires. Additionally, non-steel fibers such as polypropylene fibers, glass fibers, carbon fibers, cotton fibers, and natural fibers can be used. Fiber-reinforced concrete is typically used in shotcrete, sidewalk construction, slabs on ground, tunnel wall reinforcement, and retaining structures.
Advantages of Using Reinforced Concrete
By now, based on the introduction of various types of concrete and their applications, you should be somewhat aware of the advantages of these concretes. However, reinforced concrete includes more advantages, which we will examine further below.
-
Ease of Construction
Using reinforced concrete in construction is relatively simpler compared to steel, and it requires less skilled labor for formwork installation and concrete pouring.
-
Load-Bearing Capacity
As mentioned earlier, reinforced concrete has much higher tensile and compressive strength compared to ordinary concrete. This feature has made reinforced concrete much more commonly used in construction.
-
Fire Resistance
In general, concrete is very resistant to fire and does not catch fire. Reports indicate that concrete can withstand heat for 2 to 6 hours, allowing for evacuation and rescue operations during fires.
-
Flexibility
Another incredible advantage of reinforced concrete is its flexibility, which allows architects and builders to construct in various designs. Since concrete can be shaped by installing different molds, they can easily shape the concrete into any form they desire.
-
Seismic Resistance
With proper design and execution, reinforced concrete can be confidently relied upon for its resistance to earthquakes.
(Read ways to retrofit a building.)